TIPS and Inflation: What to Know Now

Inflation remains elevated and has been moving higher lately, likely raising some concerns about how to protect fixed income portfolios from rising consumer prices.
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities, or TIPS, can help protect against inflation since their principal values are indexed to the Consumer Price Index (CPI). When considering TIPS, however, it's important to understand their unique characteristics and complex nature. In this article, we'll cover TIPS' key characteristics, and then focus on three key considerations for investors today:
- Positive "real" yields
- Breakeven rates that are below the current level of inflation, and
- Why TIPS can protect against inflation over the long run but shouldn't be considered a short-term inflation "hedge."
TIPS explained
TIPS are a type of Treasury security whose principal value is indexed to inflation. When inflation rises, the TIPS' principal value is adjusted up. If there's deflation, then the principal value is adjusted lower. Like traditional Treasuries, TIPS are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
The coupon payments are based on a percent of the adjusted principal, so investors can benefit from higher income payments when inflation is rising, as well.
At maturity, however, a TIPS investor would receive either the adjusted principal or the original principal value at issuance. In other words, TIPS won't pay back less than their initial principal value at maturity.
The table below illustrates how the principal value and coupon payments would rise if inflation averaged 3% every year for a hypothetical five-year TIPS. While the initial principal value is $1,000, after one year that principal value would grow to $1,030. The investor would still earn a coupon payment based on the 1.0% coupon rate, but because the principal value would have risen, the coupon payment would be $10.30 at the end of year one. By maturity, the principal value would rise to $1,159 if inflation continued to average 3% per year.
Principal adjustment and coupon payments for a hypothetical five-year TIPS
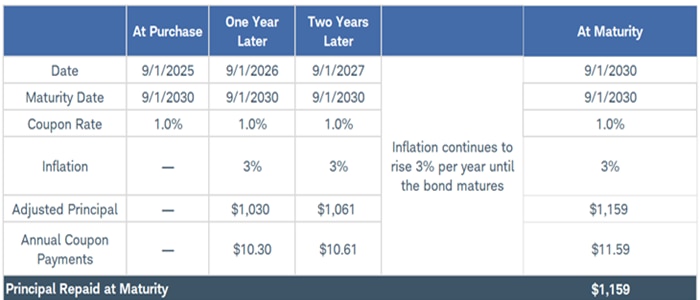
Source: Schwab Center for Financial Research.
The initial hypothetical TIPS principal value is $1,000. For simplicity, this example shows an annual coupon rate, but TIPS make semiannual interest payments. The annual coupon payment equals the fixed coupon rate multiplied by the adjusted principal value. This hypothetical example is only for illustrative purposes.
Here are three considerations for those considering TIPS today:
1. Positive real yields. Like most high-quality bond yields, TIPS yields are generally at the high end of their 15-year trading ranges. More importantly, TIPS yields are positive, meaning investors who hold individual TIPS to maturity can earn a positive inflation-adjusted yield regardless of the inflation rate.
TIPS yields are "real" yields, already accounting for inflation. The annual rate of inflation over the life of a TIPS ultimately would be added to the stated yield when held to maturity to come up with the annualized "nominal" return. If inflation were to average 3% for the next five years, for example, that 3% inflation rate would get added to the roughly 1.2% "real" yield that a five-year TIPS offers today, resulting in a nominal return of 4.2% annually. The higher (or lower) inflation comes in, the higher (or lower) that nominal total return would be.
Here's another way to think about TIPS yields: If held to maturity, TIPS should outperform inflation on an annualized basis by a magnitude of that yield. That can be an important concept for investors who are worried that inflation will remain very elevated over the short run or if it were to continue the upward trend seen over the last few months.
The chart below focuses on five-year TIPS, but yields for most other maturities are near the high end of their 15-year ranges, as well. The two- and 10-year TIPS yields were 1.0% and 1.7%, respectively, in mid-September.
TIPS yields are at the high end of their 15-year range
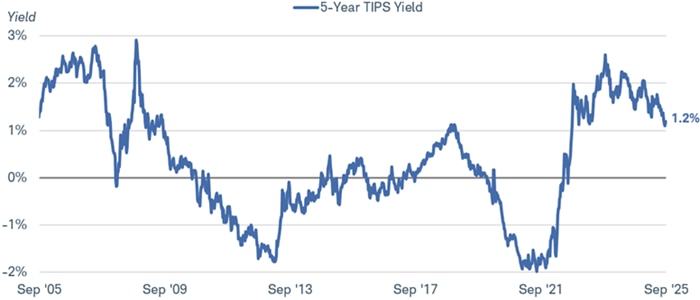
Source: Bloomberg, using weekly data from 9/19/2005 through 9/19/2025.
US Generic Govt TII 5 Yr (USGGT05Y Index). Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
"Real" yields initially rose sharply in 2022 as the Federal Reserve raised its benchmark interest rate to try to cool inflation. High real interest rates make it more attractive for consumers to save than spend, and more difficult for businesses to borrow, hire, and invest. But positive real yields can present investors an opportunity to beat inflation going forward.
2. Breakeven rates. The difference between TIPS yields and yields offered by traditional Treasuries is important to consider when evaluating TIPS. That difference is known as the "breakeven inflation rate." It can be considered a hurdle rate when trying to determine if a TIPS or a traditional Treasury will outperform the other given an expected inflation rate.
The breakeven rate is the rate that inflation, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), would need to average over the life of the TIPS for it to outperform a traditional Treasury security. If the CPI averaged more than that breakeven rate, investors would have been better off in a TIPS; if it were below, a traditional Treasury would have made more sense.
The five-year breakeven rate is shown in the chart below. At 2.5%, inflation would need to average 2.5% or more over the next five years for a five-year TIPS to outperform a nominal Treasury. That's still below the current rate of inflation, and recent inflation releases have shown that inflation has begun to reaccelerate a bit lately. The year-over-year change in headline CPI rose to 2.9% in August 2025, up from 2.3% in April. The core CPI, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, has increased as well, rising by 3.1% in the 12 months ending August 2025. The 2.5% breakeven rate is currently at the high end of the 15-year range but it's below the current inflation rate.
Five-year TIPS breakeven rate
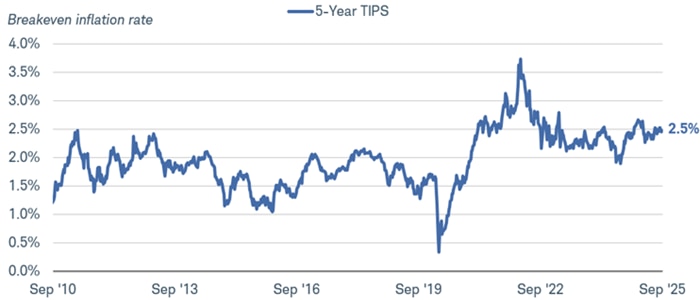
Source: Bloomberg, using weekly data from September 12, 2010 through September 12, 2025.
US Generic Govt TII 5 Yr (USGGBE05 Index). Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
3. Inflation protection is not the same thing as a short-term inflation "hedge." TIPS principal values adjust up (or down) with changes in the CPI, but their prices can still fluctuate in the secondary market. That means short-term performance may differ from what the inflation rate suggests. This happened in 2022 and 2023, as TIPS indexes generally suffered negative total returns despite inflation rising to multi-decade highs.
What happened? TIPS, despite their unique characteristics, are still bonds and subject to the inverse relationship between their prices and yields. When yields rise, prices fall, and vice versa. When the Fed raised its benchmark interest rate in 2022 and 2023, the prices of many TIPS fell more than the principal value adjustment, resulting in negative total returns.
The chart below highlights the total return of the Bloomberg US TIPS Index, beginning at the end of 2020. Total returns were positive for most of 2021 as inflation rose, but price declines pulled total returns into negative territory later on in 2022. That's likely not the performance investors were expecting given that the year-over-year change in the CPI peaked at 9.1% in June 2022. The large price declines more than offset the rise in inflation-adjusted principal values. This is a key reason why TIPS can protect against inflation over the long run but shouldn't be considered an inflation "hedge" over the short run.
The combination of higher prices from falling TIPS yields and the inflation adjustments have helped boost returns lately, however, and the cumulative total return of the Bloomberg US TIPS Index since the end of 2020 is positive again.
TIPS total returns have rebounded
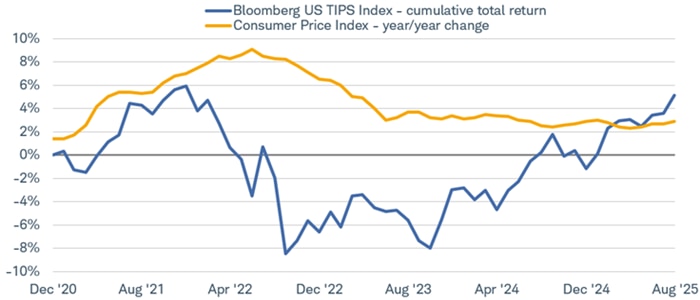
Source: Bloomberg, using daily data as of from 12/31/2020 through 8/31/2025.
Total returns assume reinvestment of interest and capital gains. Indexes are unmanaged, do not incur management fees, costs, and expenses and cannot be invested in directly. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
Those negative returns aren't indicative of the whole TIPS market, especially individual TIPS. Price fluctuations in the secondary market are temporary as long as you hold to maturity. Although TIPS prices initially fell leading up to and during the Fed's rate hiking cycle, the principal values have risen. And bond prices tend to be self-healing—barring default, a drop in price on the heels of rising yields is eventually reversed as the bond gets closer to maturity and its price amortizes toward its par value.
Consider this TIPS that was issued in October 2020, maturing in October 2025: Its inflation-adjusted value has risen to nearly $1,250 since it was issued, or nearly a 25% increase.
The inflation-adjusted principal value of TIPS has risen lately
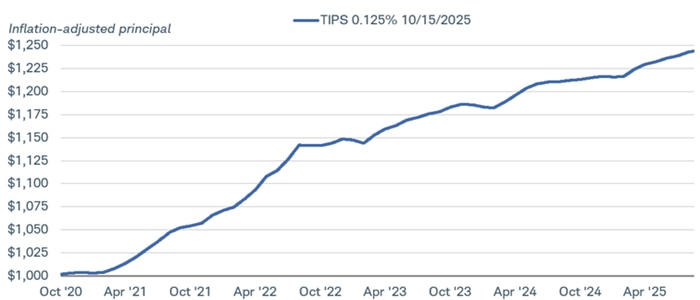
Source: Bloomberg, using daily data from 10/31/2020 through 9/15/2025.
Treasury Inflation Protected Security, 0.125% coupon rate, October 15, 2025 maturity date and US Inflation Indexed CPI Ratio 5-Year Bonds Issued October 2020. The line in the chart represents the inflation-adjusted principal value, using the CPI index ratio for this TIPS multiplied by its starting value of $1,000. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. All names and market data shown are for illustrative purposes only and are not a recommendation, offer to sell, or a solicitation of an offer to buy any security.
This material is intended for general informational and educational purposes only. This should not be considered an individualized recommendation or personalized investment advice. The securities, investment products and investment strategies mentioned are not suitable for everyone. Each investor needs to review an investment strategy for his or her own particular situation before making any investment decisions. Not intended to be reflective of results you can expect to achieve.
Although prices fell sharply when TIPS yields rose, looking at the secondary market price doesn't tell the whole story since it doesn't include the inflation adjustment. The chart below illustrates this phenomenon. The blue line represents the price of this TIPS in the secondary market; the red line multiplies that price by the TIPS' inflation index ratio. Initially prices had declined more than the inflation adjustment. The average price of this TIPS began to hold relatively steady in late 2022, then gradually increased, and has since held near $100 as it approaches its maturity in October. While the secondary market price has been holding near $100 since the beginning of 2025, the inflation-adjusted price has continued to increase given inflation's rise. This chart, and the chart above, illustrates how holding individual TIPS to maturity can help protect against inflation surges.
TIPS secondary market prices compared to its inflation-adjusted price
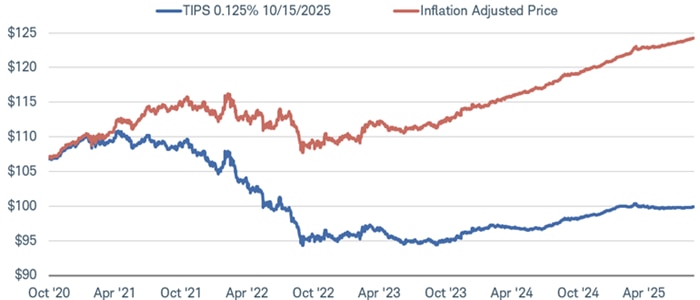
Source: Bloomberg, using daily data from 10/31/2020 through 9/15/2025.
Treasury Inflation Protected Security, 0.125% coupon rate, October 15, 2025 maturity date and US Inflation Indexed CPI Ratio 5-Year Bonds Issued October 2020. The blue line represents the secondary market price of the TIPS, while the red line multiplies that by the inflation adjustment. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. All names and market data shown are for illustrative purposes only and are not a recommendation, offer to sell, or a solicitation of an offer to buy any security. This material is intended for general informational and educational purposes only. This should not be considered an individualized recommendation or personalized investment advice. The securities, investment products and investment strategies mentioned are not suitable for everyone. Each investor needs to review an investment strategy for his or her own particular situation before making any investment decisions. Not intended to be reflective of results you can expect to achieve.
There are pros and cons to both holding individual TIPS or investing through a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF). Before investing in any fund, you should consult the fund's prospectus to understand its investment objectives, risks, charges, and expenses. One benefit that individual bonds offer—when holding bonds to maturity—is the ability to "look through" price declines in the secondary market, knowing the bonds will mature at their par value.
Consider once again the TIPS example shown above—it was issued in October 2020 and its inflation-adjusted price is up over 16% since it was issued, and that doesn't consider the semiannual interest payments. Over the same time frame, the Bloomberg US TIPS Index has gained 8.6%.
What to consider now
With inflation proving sticky and reaccelerating a bit lately, TIPS appear attractive. Real yields are still positive, and breakeven rates seem a bit low given the current "stickiness" of inflation and concerns it could remain elevated. Investors can earn higher income today with TIPS than they generally could have earned for the 10-year period leading up to the pandemic, while also helping to protect against inflation over the long-run.
We don't expect yields to rise much further, if at all, given the expectations for Fed rate cuts, so large price declines don't appear to be much of a risk right now, especially for short- and intermediate-term TIPS. But for individual TIPS holders, any potential price declines might not matter if they're held to maturity. For investors who invest in TIPS through ETFs or mutual funds, the value of the funds can fluctuate, but that doesn't mean you need to abandon your holdings. If yields were to in fact rise from here and the funds rebalance their holdings, investors may be rewarded with higher income payments to help offset potential price declines, while additional inflation increases would result in positive principal adjustments to the underlying holdings.
